What is Value-Based Care vs Fee-for-Service?
In today’s rapidly evolving healthcare landscape, understanding the difference between value-based care and fee-for-service is crucial for both patients and providers. These two distinct models shape how healthcare is delivered, paid for, and ultimately experienced.
Understanding Fee-for-Service
The traditional fee-for-service (FFS) model operates on a simple principle: providers are reimbursed for each service rendered. Whether it’s a routine check-up, a complex surgery, or a battery of tests, every procedure, consultation, and treatment has a price tag. While this approach offers a clear payment structure, it has been widely criticized for prioritizing quantity over quality.
Exploring Value-Based Care
In stark contrast, value-based care (VBC) focuses on the overall health outcomes of patients. Instead of emphasizing the number of services provided, VBC rewards providers for delivering high-quality care that improves patient health and well-being. This model incentivizes a more holistic and preventative approach, aiming to reduce unnecessary procedures and hospital readmissions.
 Illustration of Value-Based Care Model
Illustration of Value-Based Care Model
Key Differences: Value-Based Care vs. Fee-for-Service
The core distinction lies in how success is measured. FFS thrives on volume, while VBC prioritizes value. This fundamental difference plays out in several key areas:
- Payment structure: FFS reimburses for individual services, potentially encouraging overtreatment. VBC rewards providers for meeting quality standards and achieving better patient outcomes, promoting efficiency and effectiveness.
- Focus of care: FFS tends to center around treating existing conditions. VBC emphasizes preventative care, chronic disease management, and overall well-being, aiming to keep patients healthy and out of the hospital.
- Patient experience: Under FFS, patients might experience fragmented care from multiple providers. VBC encourages care coordination and collaboration among providers, leading to a more seamless and patient-centered experience.
The Benefits of Value-Based Care
The shift towards VBC promises numerous benefits:
- Improved Patient Outcomes: By focusing on quality and prevention, VBC aims to improve patient health and well-being, reducing the incidence and severity of diseases.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: By promoting efficiency and minimizing unnecessary procedures and hospitalizations, VBC has the potential to lower overall healthcare expenditures.
- Enhanced Patient Satisfaction: The emphasis on care coordination and a holistic approach to health can lead to a more positive and satisfying patient experience.
Challenges and Considerations
While the promise of VBC is significant, several challenges need to be addressed:
- Data Collection and Analysis: Effective VBC relies on robust data collection and analysis to track outcomes and measure performance, requiring significant investment in health information technology.
- Performance Measurement and Reporting: Developing standardized metrics to assess quality and outcomes can be complex, requiring ongoing refinement and collaboration among stakeholders.
- Payment Reform and Incentives: Transitioning from FFS to VBC necessitates changes in payment models and incentives to align financial rewards with quality and value.
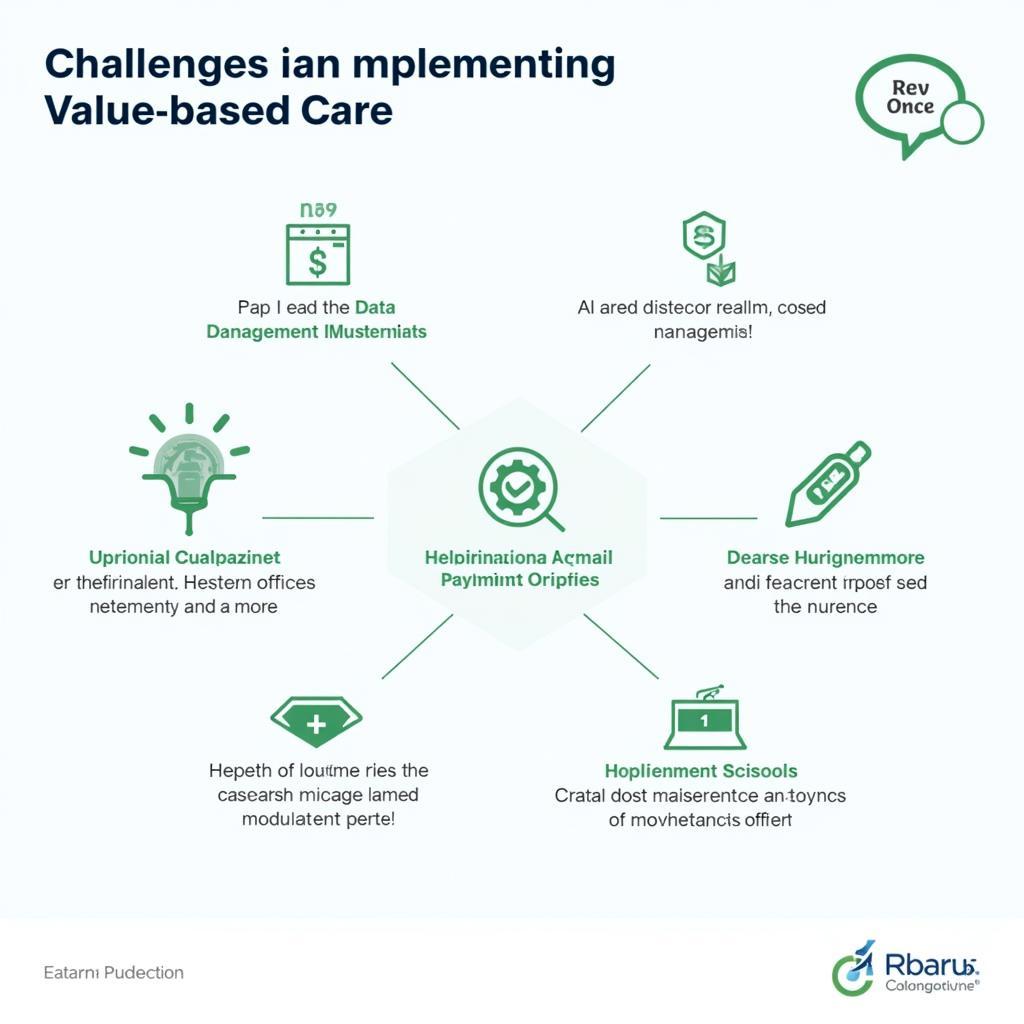 Challenges and Considerations in Value-Based Care
Challenges and Considerations in Value-Based Care
The Future of Healthcare Delivery
The movement towards VBC represents a significant paradigm shift in healthcare. By aligning incentives with value and prioritizing patient outcomes, VBC has the potential to transform how healthcare is delivered, financed, and experienced. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, embracing the principles of VBC will be crucial for achieving a more sustainable, efficient, and patient-centered healthcare system.
FAQ
1. What is the main difference between value-based care and fee-for-service?
The key difference lies in how they measure success. FFS rewards the quantity of services, while VBC prioritizes the quality of care and patient outcomes.
2. How does value-based care impact patients?
VBC aims to improve patient health outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and enhance patient satisfaction through a more holistic and preventative approach.
3. What are some examples of value-based care models?
Examples include Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs), bundled payments, and pay-for-performance programs.
4. What are the challenges of implementing value-based care?
Challenges include data management, performance measurement, payment reform, and ensuring equitable access to care.
5. What is the future of value-based care?
VBC is expected to play an increasingly important role in healthcare, driving innovation and transforming the industry towards a more value-driven approach.
Do you have other car service related questions?
Here are some other topics you might find helpful:
- How often you have to service your car
- Where should you service you new car
- Should i save service my car every year
If you need further assistance, don’t hesitate to contact our 24/7 support team via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880 or Email: [email protected]. We’re always here to help!

