What is the Primary Payer for Acute-Care Hospital Services?
Understanding who foots the bill for acute-care hospital services is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. In the US, the landscape of healthcare financing is complex, involving a mix of public and private payers. This article will delve into the primary sources of payment for these essential services.
Navigating the complexities of healthcare billing can be daunting. For a clearer understanding of who covers acute care services, see who is the primary payer for acute care services.
Public Payers: Government Funding for Acute Care
A substantial portion of acute-care hospital services is funded by government programs. Medicare, the federal health insurance program for seniors and certain individuals with disabilities, is a significant payer. Medicaid, a joint federal and state program, provides healthcare coverage for low-income individuals and families. These two programs represent a substantial portion of hospital revenue.
Medicare’s Role in Acute Care Financing
Medicare plays a vital role in financing acute-care hospital services for eligible beneficiaries. Coverage includes inpatient hospital stays, diagnostic tests, and physician services related to acute care. Medicare reimbursement rates are a significant factor influencing hospital budgets.
 Medicare Acute Care Coverage
Medicare Acute Care Coverage
Medicaid and its Contribution to Acute Care Services
Medicaid, while jointly funded by the federal government and individual states, also plays a significant role in covering acute-care hospital services. Eligibility criteria and coverage specifics vary by state, but generally, Medicaid covers necessary hospital services for eligible low-income individuals and families.
Private Payers: Insurance and Out-of-Pocket Expenses
Private health insurance companies are another major payer for acute-care hospital services. Employer-sponsored health plans and individual insurance policies cover a significant portion of the population. Out-of-pocket expenses, such as deductibles, co-pays, and coinsurance, also contribute to the overall cost of acute care.
The Importance of Private Insurance in Acute Care
Private insurance plans offer various levels of coverage for acute-care hospital services. Understanding the specifics of your insurance plan is essential to navigate potential costs. This includes knowing your deductible, co-pay, and coinsurance responsibilities.
Managing Out-of-Pocket Costs for Acute Care
Out-of-pocket expenses can be a significant financial burden for individuals receiving acute-care hospital services. Understanding your insurance plan’s cost-sharing structure is crucial for managing these expenses. Financial assistance programs and payment plans may be available to help patients manage these costs.
For those curious about the financial aspects of acute care, who pays for acute care hospital services offers additional insights.
Other Funding Sources for Acute Care
While public and private payers are the primary sources of funding, other sources contribute to the financing of acute-care hospital services. These include charitable donations, grants, and supplemental insurance policies. These sources can help bridge the gap between insurance coverage and the actual cost of care.
The Role of Charitable Giving and Grants
Charitable donations and grants can provide crucial funding for hospitals to enhance their acute-care services and support patients in need. These contributions often support specific programs or initiatives within the hospital.
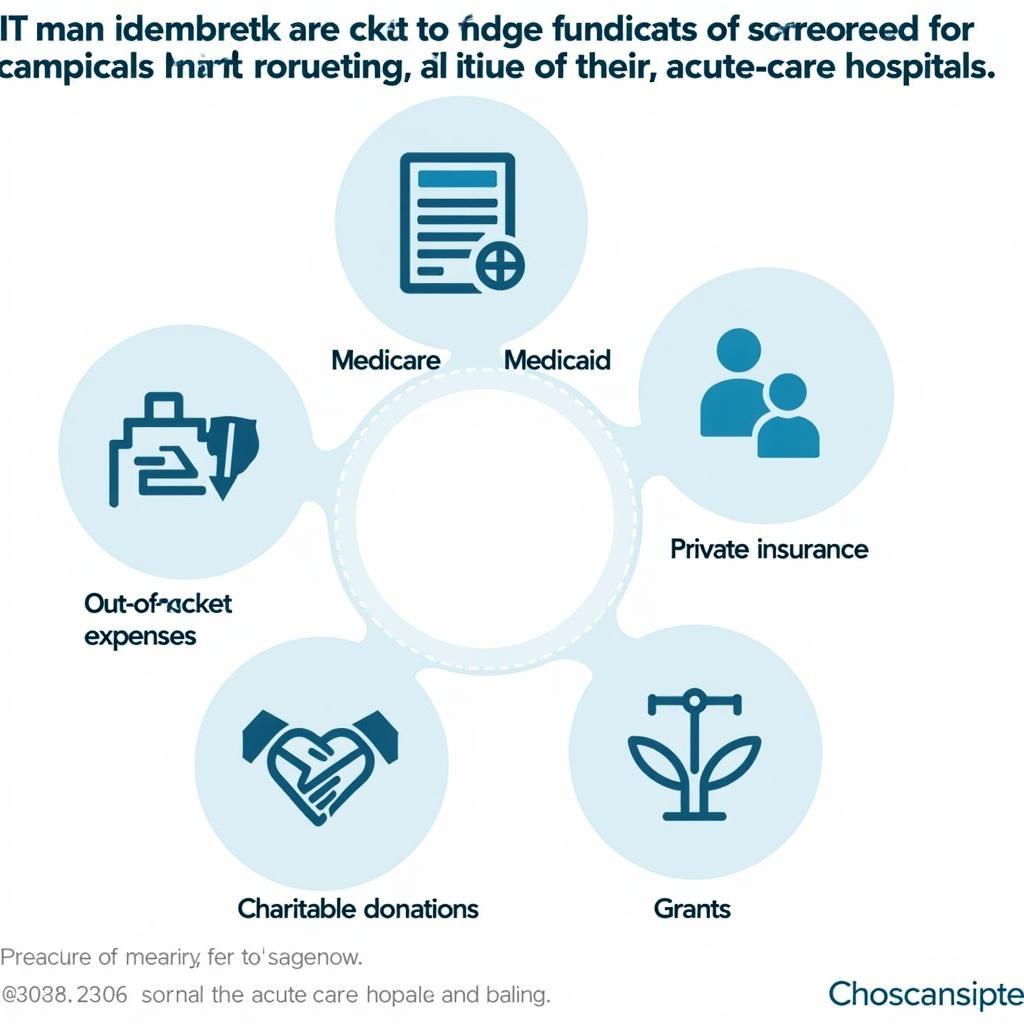 Hospital Funding Sources
Hospital Funding Sources
Conclusion: Navigating the Complexities of Acute Care Financing
Understanding who pays for acute-care hospital services is essential for both patients and healthcare providers. The complex interplay of public programs like Medicare and Medicaid, private insurance, and out-of-pocket expenses requires careful navigation. Being informed about these funding sources is key to managing the financial aspects of acute care.
FAQs
- What is acute care?
- What is the difference between Medicare and Medicaid?
- How do I find out what my insurance covers for acute care?
- What are out-of-pocket expenses?
- Are there financial assistance programs available for acute care?
- How do hospital reimbursement rates work?
- What are the different types of private health insurance plans?
Common Scenarios
- Scenario 1: An elderly individual falls and breaks a hip, requiring emergency surgery and hospitalization. Medicare would be the primary payer.
- Scenario 2: A low-income individual experiences a sudden illness and requires hospitalization. Medicaid would likely be the primary payer.
- Scenario 3: An employed individual has a car accident and requires emergency care. Their private health insurance would be the primary payer.
Further Reading
Explore other related articles on our website for more information about healthcare financing and insurance.
If you need assistance, please contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, or Email: [email protected]. Our customer service team is available 24/7.