Fee-for-service and value-based care represent two fundamentally different approaches to healthcare payment and delivery. Understanding the primary difference between these models is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers navigating the evolving landscape of healthcare. In essence, fee-for-service compensates providers for each individual service performed, while value-based care focuses on rewarding providers for the overall health outcomes of their patients. This distinction has profound implications for the quality, cost, and accessibility of healthcare.
As healthcare systems grapple with rising costs and strive to improve patient outcomes, the shift towards a means of payment for health care services centered around value is gaining momentum. This transition necessitates a thorough understanding of the core distinctions between these two models and their respective impacts on the healthcare ecosystem.
Defining Fee-for-Service Healthcare
Fee-for-service (FFS) is the traditional healthcare payment model. Under FFS, providers are reimbursed for each individual service they provide, such as a doctor’s visit, test, or procedure. The more services provided, the higher the reimbursement. This system creates a potential incentive for providers to perform more services, even if they may not be strictly necessary, leading to concerns about overutilization and cost inflation. FFS models can also lead to fragmented care, as different providers may not be effectively coordinating their efforts.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fee-for-Service
While FFS has its drawbacks, it also offers certain advantages. Patients have greater flexibility in choosing their providers, and providers have more autonomy in their decision-making. However, the lack of emphasis on preventive care and coordinated treatment plans can negatively impact patient outcomes.
Understanding Value-Based Care
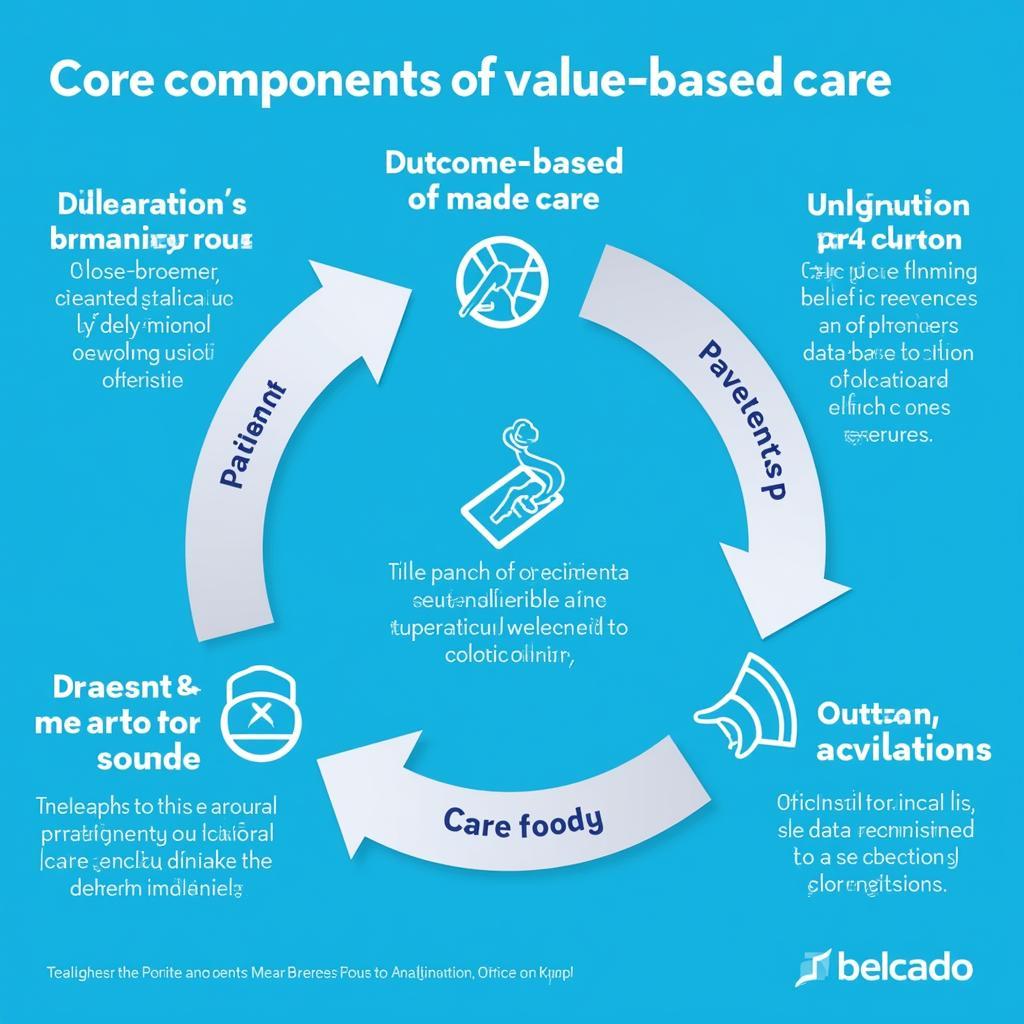
Value-based care (VBC) represents a paradigm shift in healthcare, prioritizing patient outcomes and overall health over the sheer volume of services provided. In VBC models, providers are rewarded for delivering high-quality care that leads to improved patient health and reduced costs. This approach encourages preventative care, care coordination, and a more holistic approach to patient management.
Key Features of Value-Based Care
Value-based care incorporates several key features designed to improve patient outcomes and control costs:
- Emphasis on preventative care: VBC incentivizes providers to invest in preventative measures, such as screenings and wellness programs, to keep patients healthy and avoid costly interventions later on.
- Care coordination: VBC promotes collaboration among different healthcare providers to ensure patients receive comprehensive and coordinated care, reducing redundancy and improving efficiency.
- Patient engagement: VBC empowers patients to take an active role in their own health management, providing them with the tools and resources they need to make informed decisions.
## Key Differences Between Fee-for-Service and Value-Based Care
The primary difference between fee-for-service and value-based care lies in their focus. While FFS rewards the quantity of services, VBC rewards the quality of care and patient outcomes. This fundamental difference translates into several key distinctions:
- Payment Structure: FFS pays for individual services, while VBC pays for overall health outcomes.
- Incentives: FFS incentivizes volume, while VBC incentivizes value.
- Focus: FFS focuses on treatment, while VBC focuses on prevention and long-term health management.
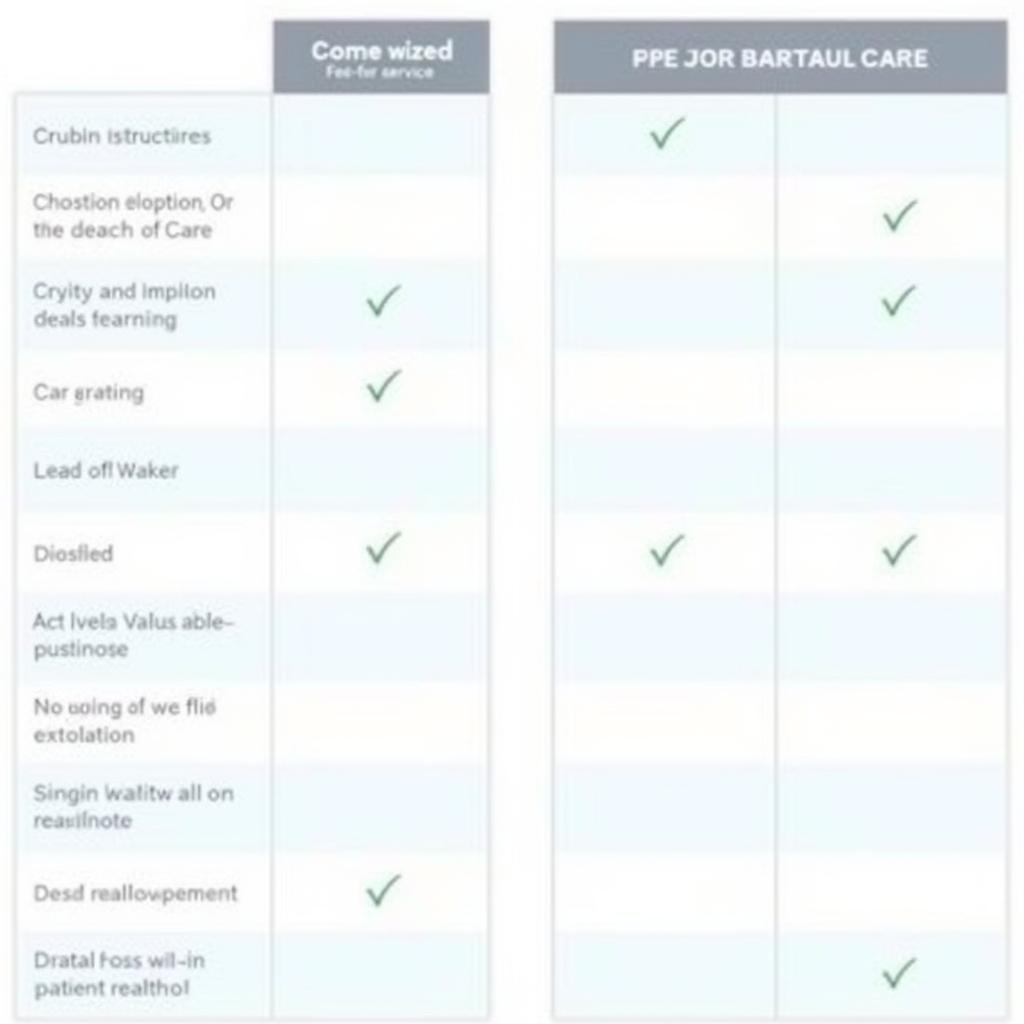
This table summarizes the key differences between FFS and VBC:
| Feature | Fee-for-Service | Value-Based Care |
|---|---|---|
| Payment | Per service | Per outcome |
| Incentive | Volume | Value |
| Focus | Treatment | Prevention |

“The shift to value-based care represents a fundamental change in how we deliver and pay for healthcare,” says Dr. Amelia Hernandez, Chief Medical Officer at Citywide Health Systems. “It’s about moving away from a system that rewards doing more to one that rewards achieving better health outcomes.”
What are the implications for patients and providers?
For patients, value-based care can mean better coordinated care, more emphasis on prevention, and potentially lower out-of-pocket costs. For providers, it requires a shift in mindset and investment in new infrastructure and technologies to support care coordination and data analysis.
“In a value-based care system, we are incentivized to keep our patients healthy and out of the hospital,” says Dr. David Lee, a primary care physician. “This aligns our goals with those of our patients, creating a true partnership in health management.”
Conclusion
The primary difference between fee-for-service and value-based care is the focus on volume versus value. While a fee-for-service health care system is one that prioritizes individual services, VBC prioritizes overall health outcomes. Understanding this key difference is essential for anyone navigating the complexities of the modern healthcare landscape. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, the shift towards value-based care is likely to accelerate, leading to more efficient, patient-centered, and cost-effective healthcare delivery.
FAQ
- What is the main difference between FFS and VBC? FFS pays per service, VBC pays for outcomes.
- Does VBC limit patient choice? Not necessarily, many VBC models still allow patients to choose their providers.
- How does VBC reduce costs? By emphasizing prevention and coordinating care, VBC aims to reduce unnecessary services and improve efficiency.
- Is VBC better for all patients? VBC aims to improve overall population health, but individual results may vary.
- How are providers reimbursed under VBC? Through various models that reward quality and cost-effectiveness.
- Are there different types of value-based care models? Yes, there are various models with different payment structures and incentives.
- What is the future of FFS? FFS is expected to decline as VBC models become more prevalent.
See also: what are health care service entities, what is managed care services.
Need more information? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected]. We have a 24/7 customer support team.