What are Cradle-to-Grave Health Care Services?
Cradle-to-grave health care services refer to a comprehensive system of health care that provides coverage and support for individuals throughout their entire lifespan, from birth to death. This approach emphasizes preventive care, early intervention, and ongoing management of health conditions to ensure optimal well-being at every stage of life.
Understanding Cradle-to-Grave Health Care
Unlike traditional health care models that primarily focus on treating illnesses as they arise, cradle-to-grave health care adopts a proactive and holistic perspective. It encompasses a wide range of services, including:
- Prenatal care: Supporting the health of both mother and child during pregnancy.
- Pediatrics: Providing routine checkups, vaccinations, and developmental screenings for children.
- Adult primary care: Offering preventive screenings, health education, and management of chronic conditions.
- Geriatric care: Addressing the unique health needs of older adults, including chronic disease management, fall prevention, and cognitive support.
- End-of-life care: Providing compassionate and dignified care for individuals nearing the end of their lives, including pain management, emotional support, and hospice services.
Benefits of a Cradle-to-Grave Approach
Adopting a cradle-to-grave health care system offers numerous benefits for individuals, communities, and health care systems as a whole:
Improved Health Outcomes: By emphasizing preventive care and early intervention, cradle-to-grave health care can help prevent or delay the onset of chronic diseases, leading to improved overall health and well-being.
Reduced Health Care Costs: Investing in preventive care and early intervention can ultimately lead to lower health care costs in the long run by reducing the need for expensive treatments and hospitalizations.
Increased Life Expectancy: Countries with strong cradle-to-grave health care systems often have higher life expectancies due to the focus on promoting health and preventing disease throughout the lifespan.
Greater Health Equity: Cradle-to-grave health care strives to provide equitable access to quality care for all individuals, regardless of their socioeconomic status, ethnicity, or geographic location.
Key Elements of Cradle-to-Grave Health Care
Successful implementation of a cradle-to-grave health care system relies on several key elements:
Universal Coverage: Ensuring that all citizens have access to essential health care services, regardless of their ability to pay.
Integrated Care: Coordinating care across different providers and settings to ensure seamless transitions and prevent gaps in service.
Focus on Prevention: Prioritizing preventive measures, such as vaccinations, screenings, and health education, to reduce the incidence of preventable diseases.
Data-Driven Decision-Making: Utilizing health data to identify trends, track outcomes, and inform policy decisions to continuously improve the effectiveness of the system.
Challenges and Considerations
While cradle-to-grave health care offers significant advantages, there are also challenges to consider:
Funding and Sustainability: Providing comprehensive health care coverage throughout the lifespan requires substantial financial resources and careful planning to ensure long-term sustainability.
Workforce Shortages: Meeting the demand for a wide range of health care services requires a well-trained and adequately staffed health care workforce, which can be a challenge in some areas.
Technological Advancements: Keeping pace with rapidly evolving medical technologies and integrating them into the health care system can be complex and costly.
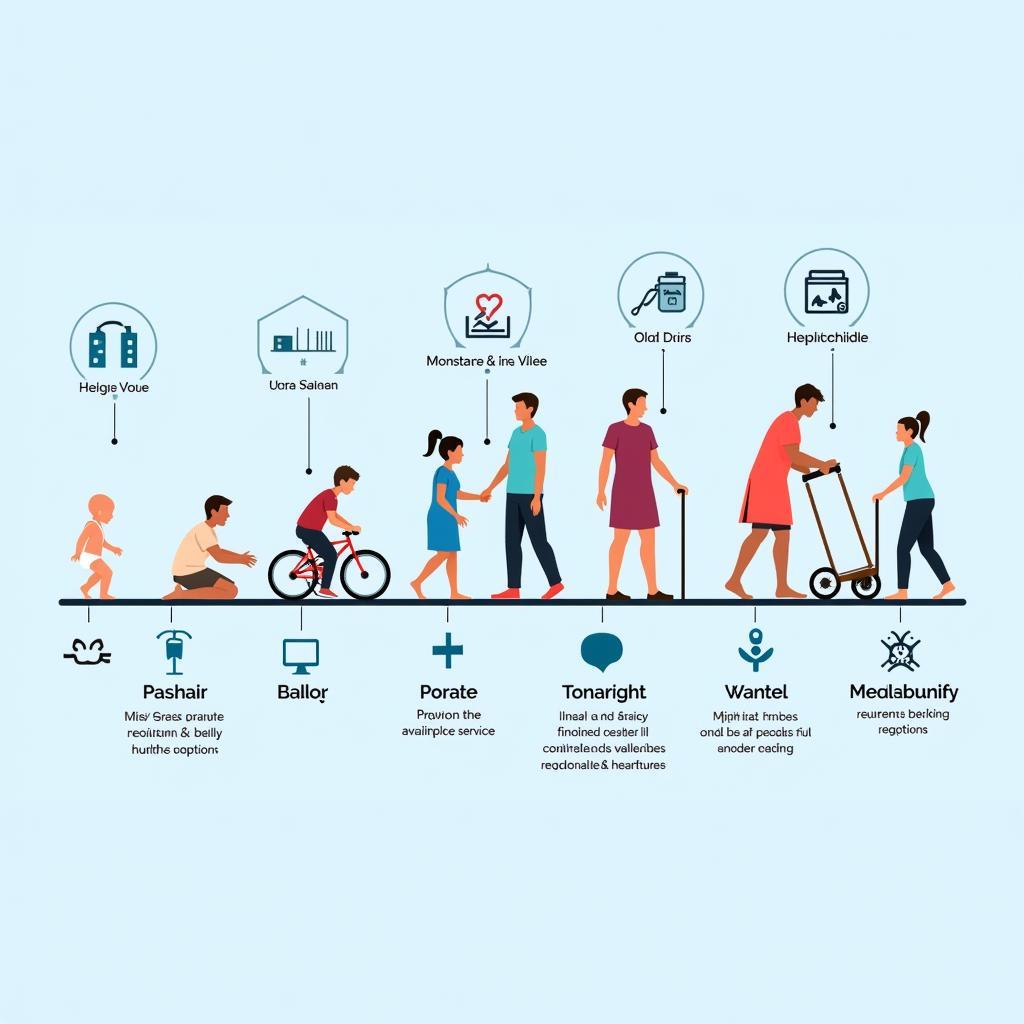 Cradle-to-Grave Healthcare Model Illustration
Cradle-to-Grave Healthcare Model Illustration
Cradle-to-Grave Health Care Around the World
Different countries have implemented cradle-to-grave health care systems with varying degrees of success. For example:
- United Kingdom: The National Health Service (NHS) provides universal health care coverage to all residents, funded primarily through taxation.
- Canada: Each province and territory has its own publicly funded health care system, providing universal coverage for medically necessary services.
- Sweden: Known for its strong social safety net, Sweden offers universal health care coverage with low out-of-pocket costs for patients.
The Future of Cradle-to-Grave Health Care
As populations age and health care needs become more complex, the importance of cradle-to-grave health care is likely to grow. Advancements in technology, such as telemedicine and artificial intelligence, have the potential to improve access to care, enhance efficiency, and personalize treatments.
 Future of Healthcare Technologies
Future of Healthcare Technologies
Conclusion
Cradle-to-grave health care services represent a comprehensive and proactive approach to healthcare that prioritizes well-being throughout the entire lifespan. By emphasizing prevention, early intervention, and integrated care, this model aims to improve health outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and enhance overall quality of life. While challenges remain in terms of funding, workforce, and technological advancements, the concept of cradle-to-grave health care continues to evolve and adapt to the changing needs of individuals and societies worldwide.

