How Are Hospitals Reimbursed for Their Services and Care?
Navigating the complex world of hospital reimbursement can feel like deciphering a foreign language. Understanding how hospitals receive payment for the critical services they provide is essential for both patients and healthcare providers.
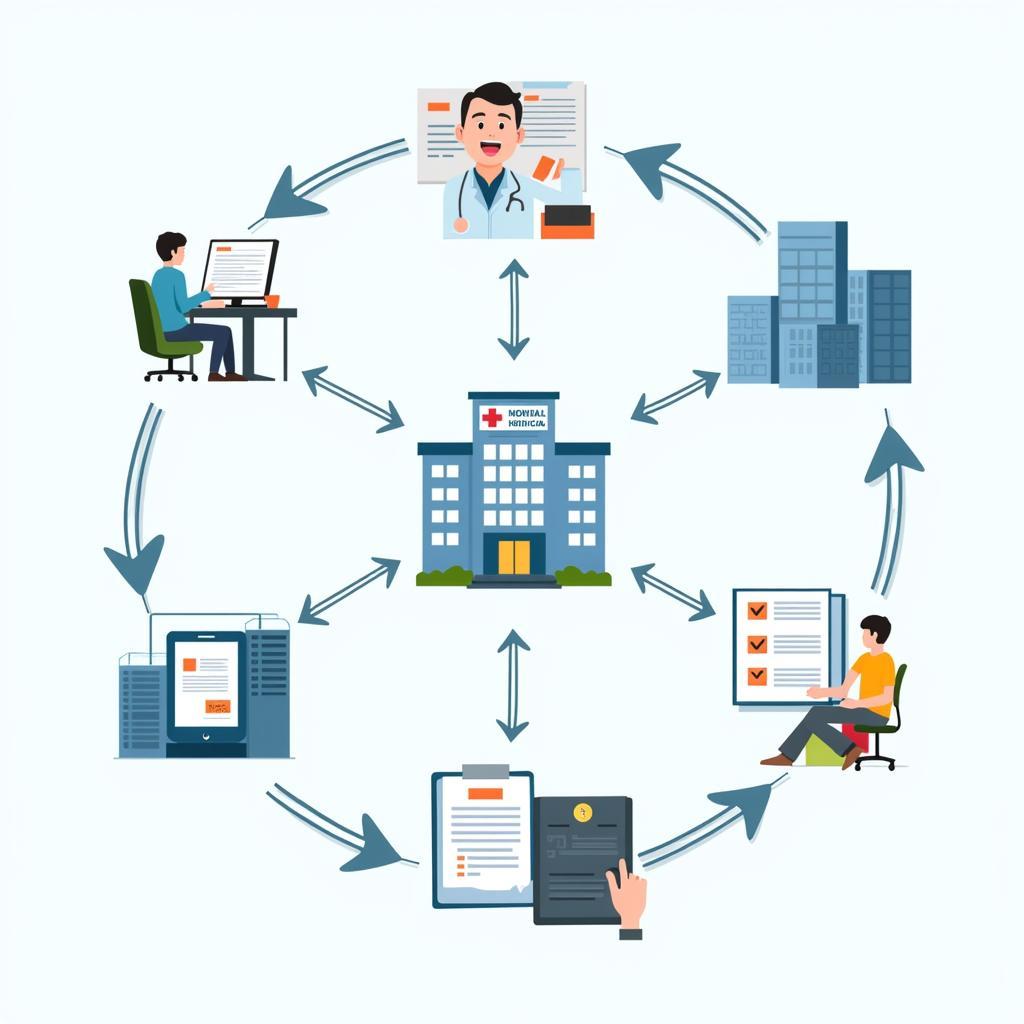 Hospital Billing Process
Hospital Billing Process
The Intricate Dance of Hospital Reimbursement
Hospitals don’t simply send a bill for services rendered and receive a lump sum payment. Instead, they engage in a multi-faceted process involving various stakeholders, primarily insurance companies and government programs like Medicare and Medicaid.
Key Players in Hospital Reimbursement
- Patients: The recipients of care, responsible for costs not covered by insurance.
- Hospitals: Healthcare providers delivering medical services.
- Insurance Companies: Private entities offering health insurance plans.
- Government Programs: Medicare (for seniors) and Medicaid (for low-income individuals).
Decoding the Reimbursement Models
Hospitals utilize different reimbursement models, each with its own set of complexities:
1. Fee-for-Service
This traditional model reimburses hospitals for each individual service provided. While seemingly straightforward, it can incentivize overtreatment and inflate healthcare costs.
2. Value-Based Reimbursement
This model rewards hospitals for the quality and efficiency of care provided. Incentives are tied to patient outcomes, encouraging hospitals to prioritize effective and cost-conscious care.
 Value-Based Healthcare Model
Value-Based Healthcare Model
3. Bundled Payments
This model offers a single, comprehensive payment for an episode of care, such as a hip replacement surgery. This encourages hospitals and providers to collaborate and streamline care, minimizing unnecessary costs and improving patient outcomes.
The Role of Medical Coding and Billing
Accurate medical coding and billing are crucial for hospitals to receive appropriate reimbursement. This involves translating medical procedures and diagnoses into standardized codes used for billing purposes. Errors in coding can lead to denied claims and revenue loss.
Challenges in Hospital Reimbursement
- Denials and Underpayments: Insurance companies may deny claims or reimburse less than the billed amount, requiring hospitals to navigate appeals and negotiations.
- Complex Regulations: Reimbursement policies and regulations are constantly evolving, requiring hospitals to stay informed and adapt their billing practices.
- Increasing Healthcare Costs: The rising cost of healthcare continues to strain reimbursement systems, impacting both hospitals and patients.
The Future of Hospital Reimbursement
The healthcare landscape is shifting towards value-based care and alternative payment models. This transition aims to:
- Improve Patient Outcomes: Focus on quality care and patient satisfaction.
- Control Healthcare Costs: Incentivize efficiency and reduce unnecessary spending.
- Enhance Care Coordination: Promote collaboration among providers for seamless patient care.
Conclusion
Hospital reimbursement is a multifaceted process crucial for the financial stability of healthcare systems and access to quality care. Understanding these complexities empowers patients to navigate their own healthcare expenses and encourages informed dialogue about the future of healthcare financing.

