Understanding a Fee for Service Health Care System
A Fee For Service Health Care System is one that bills patients for each individual service provided. This system, while common, has its pros and cons, and understanding them is crucial for navigating healthcare decisions. This article dives deep into the intricacies of fee-for-service healthcare, exploring its impact on patients, providers, and the overall healthcare landscape.
What is a Fee for Service Health Care System and How Does it Work?
A fee-for-service model operates on a straightforward principle: healthcare providers charge a separate fee for every service rendered, from doctor visits and tests to procedures and hospital stays. This differs from other models like capitation or value-based care, where providers receive a set amount per patient or are reimbursed based on quality metrics. In a fee-for-service system, the more services provided, the higher the revenue generated.
This system has been the dominant model in the US for decades, influencing how healthcare is delivered and received. But as healthcare costs continue to rise, there’s increasing scrutiny on whether fee-for-service is still the most effective approach.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a Fee for Service Health Care System
Like any system, fee-for-service has its benefits and drawbacks. Understanding both sides is critical for informed decision-making.
Advantages of Fee-for-Service:
- Greater Choice and Flexibility: Patients often have more freedom to choose their doctors and specialists without network restrictions.
- Clear Billing: Itemized bills detail each service and its corresponding cost, enhancing transparency.
- Incentive for Provider Availability: Providers may be more willing to see patients, especially those with complex or chronic conditions requiring frequent visits.
Disadvantages of Fee-for-Service:
- Potential for Overutilization: The incentive to provide more services can lead to unnecessary tests, procedures, and specialist referrals, driving up costs and potentially exposing patients to risks.
- Fragmented Care: Coordination of care among multiple providers can be challenging, leading to gaps in communication and potential errors.
- Administrative Burden: Both providers and patients face significant administrative work related to billing and claims processing.
“In a fee-for-service system, the focus can shift from delivering necessary care to maximizing billable services,” says Dr. Emily Carter, a leading healthcare economist at the Institute for Healthcare Reform. “This can create a conflict of interest that ultimately harms both patients and the healthcare system.”
Alternatives to Fee-for-Service Healthcare
As concerns about cost and quality of care grow, alternative payment models are gaining traction. These models aim to shift the focus from volume to value.
- Value-Based Care: Providers are reimbursed based on the quality and effectiveness of care they deliver, incentivizing better patient outcomes. a fee-for-service health care system is one that
- Capitation: Providers receive a fixed amount per patient, regardless of the services provided. what is receipt of health care services
- Bundled Payments: A single payment covers a group of related services for a specific condition or episode of care.
These models aim to address some of the shortcomings of fee-for-service by encouraging preventative care, care coordination, and efficient resource utilization.
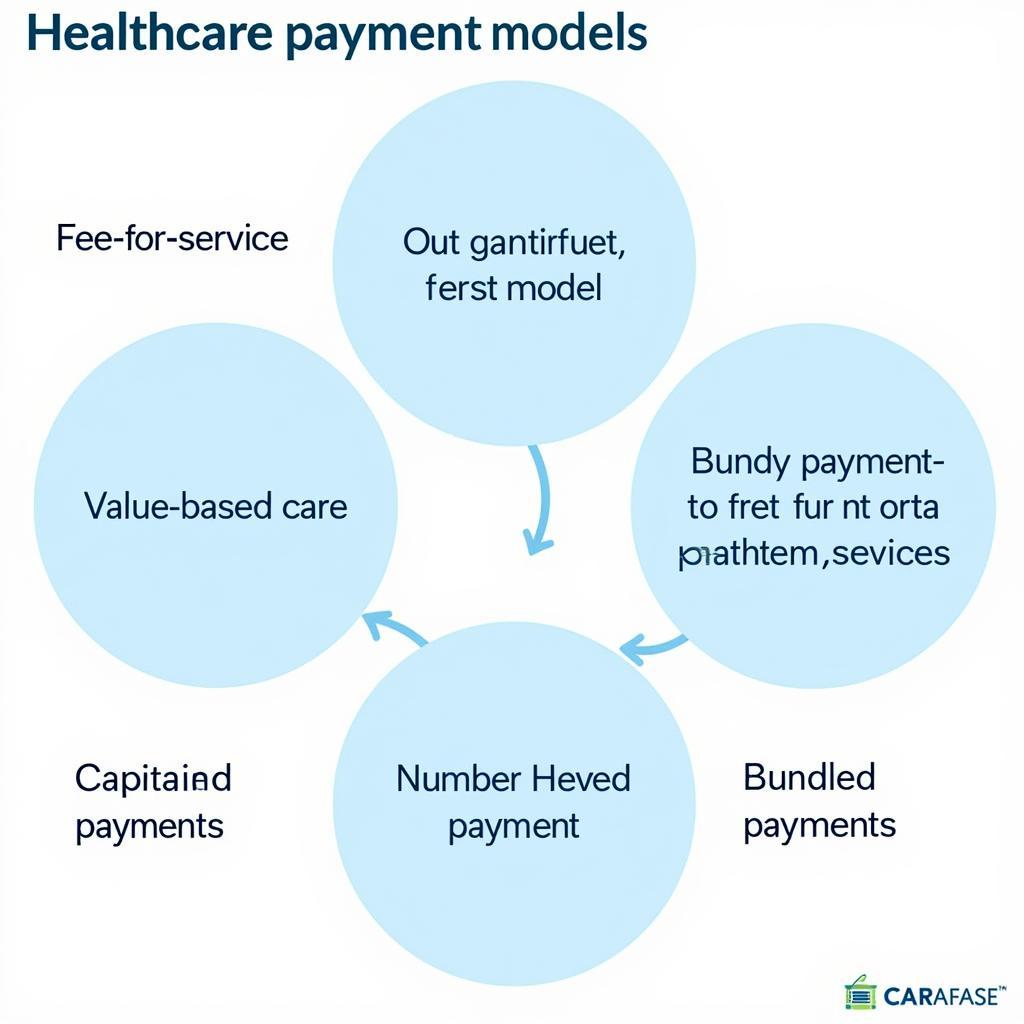 Alternative Healthcare Payment Models Explained
Alternative Healthcare Payment Models Explained
What Does the Future Hold for Fee-for-Service Healthcare?
While fee-for-service remains a significant part of the healthcare landscape, it is unlikely to remain the dominant model. what things do i need to service my car The shift towards value-based care and other alternative payment models is gaining momentum as payers and policymakers seek to control costs and improve the quality of care. how to deliver a good customer care service “The future of healthcare reimbursement lies in rewarding value over volume,” asserts Dr. Michael Peterson, Director of Healthcare Policy at the National Healthcare Institute. “This means paying for outcomes, not individual services.” can i.use the va for non-service related care
Conclusion
Understanding a fee for service health care system is essential for navigating the complex world of healthcare. While it offers certain advantages, its inherent drawbacks have led to the rise of alternative payment models focused on value and quality. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, staying informed about these changes will empower you to make informed decisions about your health and care.
Need car service support? Contact us via WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected] or visit us at 456 Oak Avenue, Miami, FL 33101, USA. Our customer service team is available 24/7.

